Innovation

Experience Powers Us
We’ve been powering America with clean natural gas for more than a century, so we know what it takes to fuel progress.

Scale. Reliability. Growth.
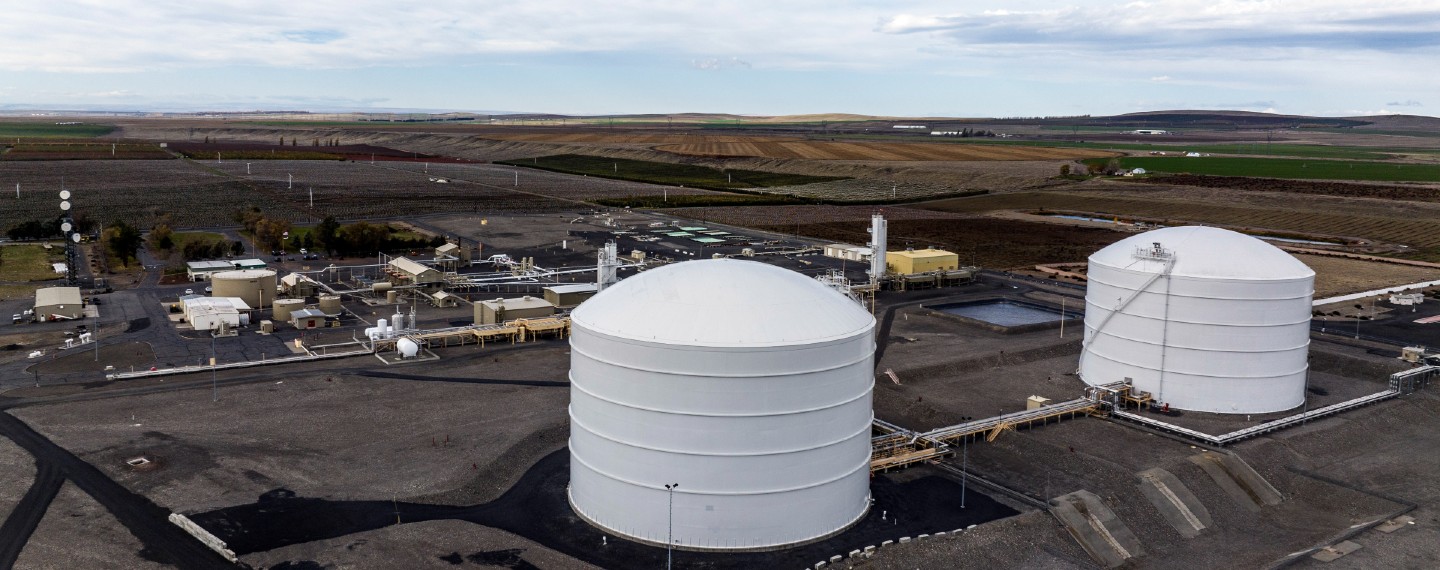
Critical U.S. natural gas infrastructure serving today’s energy needs

2022 Sustainability Report
With our strong focus on sustainable operations, we are committed to leveraging our large-scale natural gas network for the benefit of tomorrow and generations to come.

Careers
At Williams, we make clean energy happen. And so can you. Bring your energy to ours.
Latest News

Benefits of U.S. LNG
We make clean energy happen
We make clean energy happen by being the best-in-class operator of the critical infrastructure that supports a clean energy future.


Our Commitment to Sustainability
We work to remain responsible stewards of the resources entrusted to us by proactively managing our environment, social, and governance performance.
The Future of Energy

Learn more about what we are doing right here, right now.
Williams is focused on practical and immediate opportunities to reduce emissions and scale renewables – while looking forward to and anticipating future innovations and technologies. Learn more.